
Momentum (GCSE) — the science sauce
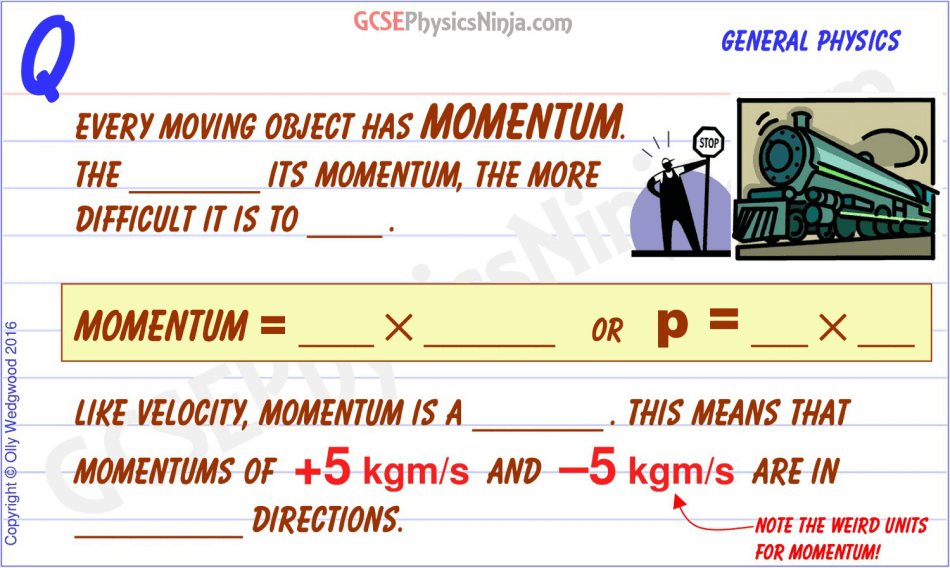
Momentum is the product of a moving object's and velocity . \ (\text {Momentum} = \text {mass}\times \text {velocity}\) The symbol for momentum is \ (p\) so this can also be written as: \.

KS4/GCSE Physics Momentum & Collisions Revision Resources For Dyslexics
Learn about and revise momentum, conservation of momentum, and the relationship between force and momentum in collisions with GCSE Bitesize Physics.
44. Momentum Equation
AQA GCSE Physics Revision. January mocks on the horizon? Kick-start your revision with our 2-day online Mock Preparation courses. Suitable for separate and combined science higher level students. Science AQA GCSE and Edexcel IGCSE - 2-3rd and 5-6th January.
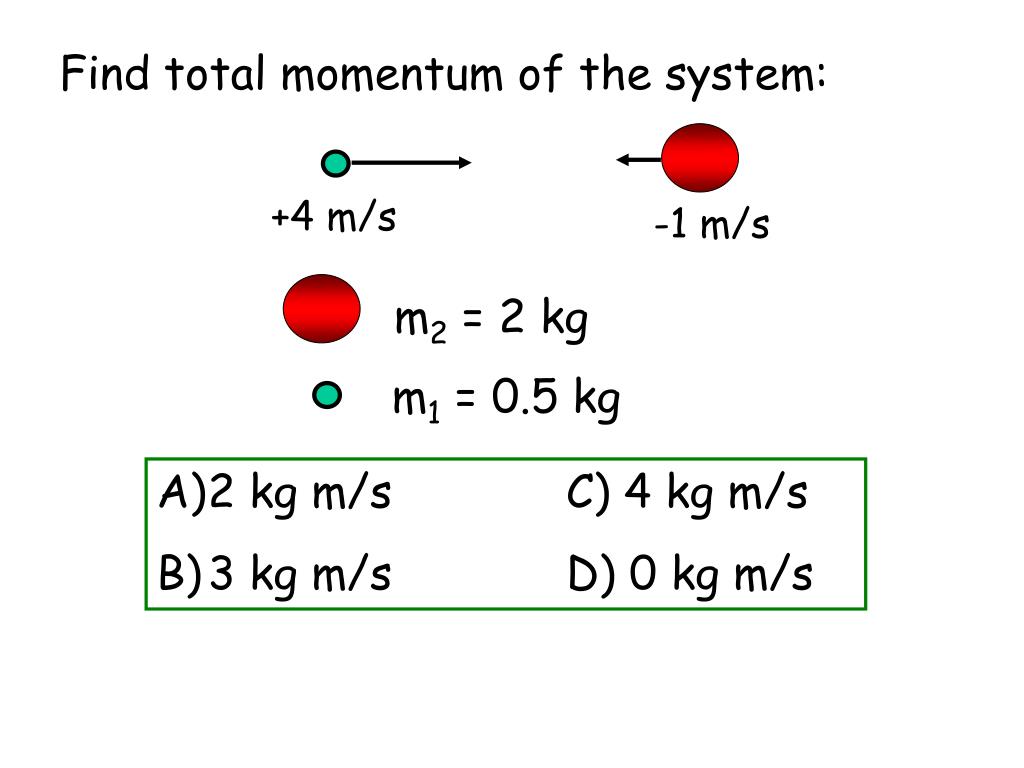
PPT System Total Momentum PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4272286
PeterPremium. Private GCSE Physics Tuition. I specialise in A Level Physics primarily AQA, but also all other Boards. I also teach all A Level Maths subjects. At GCSE and iGCSE, I teach maths, further maths and physics. I also assist A Level students with entrance tests such as the Engineering Tests for Cambridge etc.
Y11 Additional GCSE Physics Momentum
velocity . Momentum is also a quantity - this means it has both a magnitude and an associated direction. For example, an elephant has no momentum when it is standing still. When it begins to.

KS4/GCSE Physics Momentum & Collisions Revision Resources For Dyslexics
When a force acts on an object that is moving, or able to move, there is a change in momentum : in equations, change in momentum is shown as m∆v ∆v is the change in velocity (∆ is the Greek.

GCSE Physics Momentum
Momentum keeps an object moving in the same direction, making it difficult to change the direction of an object with a large momentum Since velocity is a vector this means that the momentum of an object also depends on its direction of travel This means that momentum can be either positive or negative

AQA GCSE Physics 2 3 Work Energy Momentum
GCSE OCR Gateway Momentum, work and power - OCR Gateway Momentum - Higher Momentum can be thought of as the product of mass and velocity. Momentum helps explain some of the most important.
Momentum GCSE Physics P2 Edexcel YouTube
Topic Specification Momentum Revision Momentum Momentum is a property of all moving objects. It depends on mass and velocity. Momentum Momentum is a vector, meaning it has magnitude and direction. It is defined by the equation: \textcolor {aa57ff} {p = mv} p = mv \textcolor {aa57ff} {p} p is the momentum in kilogram metres per second

Momentum with Questions and Model Answers GCSE Physics Revision YouTube
With what force did she hit the ball? We first need to work out the momentum of the ball using the equation momentum = mass x velocity. Remember that mass is always in kg. Momentum = 0.05 kg x 70 m/s = 3.5 kg m/s We can then use the equation force = change in momentum / time Force = 3.5 / 5 = 0.7 N

How to Calculate Momentum (p=mxv) GCSE Physics (91) YouTube
Momentum for AQA GCSE Physics This page covers the following topics: 1. Momentum 2. Momentum and force 😀 Do you have a revision plan? Get one and accelerate your exam preparation. GET A PLAN The momentum of a moving object can be calculated by multiplying the mass of the object by its velocity.

Momentum & Conservation of Momentum GCSE Science Physics Get To Know Science YouTube
Revising for your GCSE physics exam? Learn about momentum in this video!Music credits: https://www.bensound.com/

KS4/GCSE Physics Momentum & Collisions Revision Resources For Dyslexics
AQA GCSE 9-1 Physics Momentum Lesson. Lesson Objectives. Understand the factors that affect momentum and solve momentum problems. Success Criteria. All - Recall the factors that affect momentum and create a formula triangle. Most - Use the equation p=mv to solve a number of problems for momentum. Some - Solve problems involving the.

PPT GCSE PHYSICS MOMENTUM PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1254124
Momentum Higher Tier Only A moving object has momentum which is defined by the equation: p = mv Where: p = momentum in kilogram metre per second (kg m/s) m = mass in kilograms (kg) v = velocity in metres per second (m/s) This means that an object at rest (i.e v = 0) has no momentum

What is MOMENTUM? GCSE physics YouTube
What is Momentum? Anything that moves has momentum (see also kinetic energy ). The amount of momentum that an object has depends on how fast it is moving (its velocity) and on the mass of the object. momentum = mass x velocity. The equation is written as p = m x v where p = momentum m = mass and v = velocity. This equation is important!

GCSE Physics Momentum
Easy Medium Hard Model Answers 1a 2 marks Higher Only At a paintballing party, a group of children fire paint balls at each other using paintball guns. The paintball guns have a mass of 0.5 kg each. Each paintball inside the gun has a mass of 2.5 g. Describe and explain the momentum of the paintball before the gun is fired.